-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
-
-

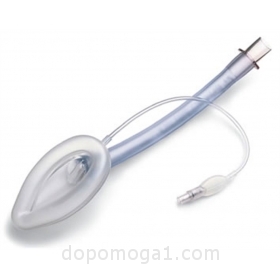
Tubes with low pressure cuffs for separate ventilation; for separate ventilation of the lungs in thoracic surgery, as well as in resuscitation with asymmetric lung involvement.
-

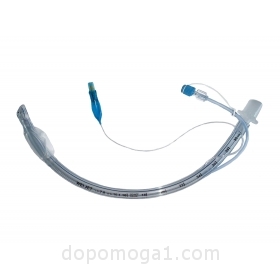
Used in general anesthesia, intensive care and with emergency care to ensure airway patency, oral intubation and mechanical ventilation. The tube is inserted into the trachea of the patient through the nose or mouth of the patient, to ensure airway patency, so that air enters the lungs.
-

Used in general anesthesia, intensive care and with emergency care to ensure airway patency, oral intubation and mechanical ventilation. The tube is inserted into the trachea of the patient through the nose or mouth of the patient, to ensure airway patency, so that air enters the lungs. The aspiration port allows you to remove the secret and sputum that accumulated in the patient's trachea.
-

Used in general anesthesia, intensive care and with emergency care to ensure airway patency, oral intubation and mechanical ventilation. The tube is inserted into the trachea of the patient through the nose or mouth of the patient, to ensure airway patency, so that air enters the lungs.
-

Used to restore airway patency, artificial ventilation, auxiliary ventilation, as well as self-breathing through the tracheostomy.
-

Used to restore airway patency, artificial ventilation, auxiliary ventilation, as well as self-breathing through the tracheostomy.
-

Used to restore airway patency, artificial ventilation, auxiliary ventilation, as well as self-breathing through the tracheostomy. The aspiration port allows you to remove the secret and sputum that accumulated in the patient's trachea.
-

Used in general anesthesia, intensive care and for emergency care to ensure airway patency, oral intubation and mechanical ventilation. The tube is inserted into the trachea of the patient through the nose or mouth of the patient, to ensure airway patency, so that air enters the lungs. Sets of single use.
-

Airway are used in general anesthesia, intensive care and in the provision of emergency care to ensure patency of the upper respiratory tract. Nasopharyngeal airways are used if one can not open the patient's mouth (cramps, etc).
-

Designed to restore patency of the airways of patients with general anesthesia and unconscious patients.
-

Designed to ensure reliable airway patency, it is an alternative to an endotracheal tube or an anesthetic mask for short-term use in anesthesia or in certain emergency conditions.
-

For masked artificial ventilation. Masks provide a comfortable and secure fit. Anatomical masks are equipped with a special soft cuff that provides a tight fit of the mask to the face of the patient with minimal effort, which is applied, creating maximum comfort for the patient and medical personnel.
-

Designed for aspiration of the tracheobronchial secretion and sputum from the respiratory tract of patients on ventilator, as well as breathing independently through the tracheostomy or endotracheal tube.
-

Manual device for artificial ventilation of lungs, applied to patients with respiratory failure. It is based on the forced air supply to the lungs by means of a mask by compressing the bag, which itself is filled. The respiratory volume depends on the degree of compression of the bag, and the frequency of air supply and minute ventilation depends on the intensity of the operator's actions.
-

Manual device for artificial ventilation of lungs, applied to patients with respiratory failure.
- 08129, Bucha distr., Kyiv region
Pertopavlivska Borshchagivka
Polstavska st. 30 - +380 44-463-74-88
- info@dopomoga1.com
Dopomoga-I
WE CARE ABOUTH YOUR HEALTH



